[tldr]
- While genes and age do play role, you can slow down and even stop the graying process with some natural hacks.
- Pigment cells called melanocytes give your hair its color. When you stop producing this melanin, hair begins to turn gray.
- Researchers recently discovered that going gray is a buildup of hydrogen peroxide in your hair particles, which bleaches your hair from the inside.
- Usually an enzyme called catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, but as you get older, catalase production starts to slow down.
- A 2016 study offered another intriguing possibility — that targeting the molecular pathways that govern hair pigment could restore hair color.
- What you can do to reverse gray hair now: try a pseudocatalase cream, load up on antioxidants, and take an anti-gray hair pill.
[/tldr]
Like most people, you probably think that gray hair is a natural part of growing older, or that it’s simply genetic. While those factors do play a role, you can slow down — and possibly even reverse — the graying process with some natural hacks. So put down the bottle of hair dye and read on to find out how to get rid of gray hair naturally.
RELATED: Get free guides, ebooks, recipes and more to supercharge your health
What causes gray hair?

“There are pigment cells called melanocytes in your hair follicles which give your hair its color, called melanin,” says Debra Jaliman, MD, author of “Skin Rules: Trade Secrets from a Top New York Dermatologist.” “When you stop producing this melanin, hair begins to turn gray.”
People typically start going gray after the age of 30 — from there, the likelihood of turning gray increases 10 to 20 percent every decade.[ref url=”https://www.loc.gov/rr/scitech/mysteries/grayhair.html”]
Sure, age and genes do play a hand in deciding when you start to go gray. But what is it exactly that causes your body to stop producing melanin? The question has stumped scientists for decades, but a handful of recent studies provide some answers.
Gray hair and catalase

In a 2009 study, researchers discovered that going gray is simply a buildup of hydrogen peroxide in your hair particles, which bleaches your hair from the inside.[ref url=”https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/02/090223131123.htm “] Yep, bottle blondes love hydrogen peroxide for its bleaching effect, but it’s also a chemical that your hair cells make naturally.
Here’s where things get interesting — usually, a hardworking enzyme called catalase breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. But as you get older, catalase production starts to slow down. The result? Hydrogen peroxide starts to accumulate in the body.
“Hydrogen peroxide plays a major role in essentially bleaching out the hair pigment centers,” says Ronald Peralta, cancer survivor and co-founder of hair supplement Nutrafol, in a recent Bulletproof Radio (iTunes) podcast episode. “Gray hair is nothing less than a reflection of a reduction of catalase enzyme, one of the more potent antioxidants.”
Catalase isn’t the only enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide. Glutathione peroxidase, the body’s master antioxidant produced by the liver, turns hydrogen peroxide into water.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3159114/ “] Because glutathione production lowers as you get older, it’s a good idea to supplement. To get more glutathione:
- Take glutathione supplements (500-1000mg on an empty stomach at bedtime)
- Add grass-fed whey protein to your diet. Research shows that taking 10 grams of whey twice a day increases glutathione levels in the body by 46 percent.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15463873″]
- Eat foods rich in vitamin C, which raises glutathione in red blood cells.[ref url=”https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article-abstract/58/1/103/4715823″]
- Exercise regularly. Working out boosts your body’s antioxidant levels, including glutathione.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17925621″]
Related: Best Supplements for Glowing Skin, Shiny Hair, and Strong Nails
Mnt signaling and gray hair

A 2016 study offered another intriguing possibility — that targeting the molecular pathways that govern hair pigment could restore hair color.[ref url=”https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(16)30405-3″] By studying stem cells in mice, scientists at New York University’s Langone Medical Center found that a signaling pathway called Edn/EdnrB interacts with other pathways, particularly the Mnt signaling pathway. This process creates more melanocytes — cells that form melanin in the skin and hair.
The study was the first to find a link between these signaling pathways and hair and skin pigment. The findings suggest that developing a drug or other therapy to target these pathways may help bring back some color to gray tresses.
What you can try now to treat gray hair
Try a pseudocatalase cream

A topical cream called PC-KUS, described as a “pseudocatalase”, works on people with vitiligo — when your skin loses its color in patches. Like gray hair, scientists believe that vitiligo is also caused by too much hydrogen peroxide in the body. The idea is that PC-KUS mimics the effects catalase, as your body’s own production of the enzyme drops. In a 2013 study, patients with vitiligo saw pigment return to their skin and eyelashes after exposing their skin with pseudocatalase to sunlight.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23629861″]
In another study, 90% of patients with vitiligo on their face and hands saw complete improvement after applying pseudocatalase, combined with sun exposure, every day, when used for at least 4 months.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7599386″]
While promising, these studies were all done with the goal of treating vitiligo, and not gray hair. So far no studies have looked at pseudocatalase’s ability to restore natural hair color. Since both gray hair and vitiligo are caused by a buildup of hydrogen peroxide in the body, researchers simply surmise that what works for vitiligo will work for gray hair.
So should you try pseudocatalase? It might be worth waiting until more solid research shows that it works to repigment hair, otherwise it could be money down the drain.
And if you prefer plant-based products, pseudocatalase might not be for you. A lot of brands use a combination of sodium bicarbonate, manganese chloride, calcium chloride, and disodium edta, along with petroleum and parabens in their pseudocatalase products. Some of those ingredients are safe, while others, like manganese chloride, are considered high hazard by the Environmental Working Group (EWG), an environmental advocacy organization.
Load up on antioxidants to treat gray hair

“Catalase is one of the more potent antioxidants,” says Peralta. “But as we get older, our antioxidant levels begin to drop.”
You can ramp up your catalase production by taking antioxidants like ashwagandha, curcumin, saw palmetto, and vitamin E, says Peralta.
In one study, ashwagandha — an ayurvedic herb — protected white blood cells in rats from free radical damage caused by hydrogen peroxide.[ref url=” http://www.phcogj.com/article/320″] In another study, 3 grams of ashwagandha powder a day for a year increased the amount of hair melanin in middle-aged men.[ref url=”http://altmedrev.com/archive/publications/5/4/334.pdf”]
You can also eat more catalase-rich foods such as broccoli, kale, cucumbers, radishes, and celery.
Pop an anti-gray hair pill

L’Oreal announced back in 2011 that it was developing a pill to treat gray hair. The cosmetics giant said the pill would use an “undisclosed” fruit extract which acts in the same way as tyrosinase-related protein 2 (TRP-2), an enzyme that protects hair pigment.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15357835″]
The company promised the pill would be natural and could be taken as a dietary supplement. The drawback? You have to take the pill every day for the rest of your life for it to keep working.
No word from L’Oreal on when the pill is set to be launched.
Other companies have already released pills that promise to reverse gray. SeroVital Hair Regeneres uses a combination of melanin and keratin (the protein that makes up your hair), along with antioxidants like cacao and turmeric, to repigment the hair and lessen hair loss. The company claims people start to see results after 60 days of taking two pills a day, coupled with a scalp massage using their serum.
The government has gone after some companies for making unsubstantiated claims about their anti-gray hair products. The Federal Trade Commission fined Go Away Grey and Get Away Grey — different supplements that promise to up your levels of catalase — for misleading consumers by claiming their products could restore natural hair color, without any scientific evidence.
Other gray hair home remedies

You can also dig around in your kitchen pantry for some natural gray hair remedies. When you’re done putting coconut oil in your pan, massage some into your scalp. In ayurveda, gray hair is caused by too much pitta dosha (aka high body heat). Ayurveda suggests massaging your scalp with oil, which helps release any excess heat and keeps your hair nourished and strong. You can also blend up an onion and apply the juice to your scalp for 30 minutes — folklore says it increases levels of catalase on the skin.
But take these home remedies with a pinch of [pink Himalayan] salt — there’s no science that says they work.
And remember, many cultures consider a sprinkling of gray — and even a full head of white hair — to be a sign of wisdom. So focus on keeping your brain sharp and your body strong — that’s what’s really going to keep you looking, and feeling, young.






 Before we jump into how ketamine works — and why it’s such an effective treatment for depression — let’s talk about what, exactly, ketamine is.
Before we jump into how ketamine works — and why it’s such an effective treatment for depression — let’s talk about what, exactly, ketamine is.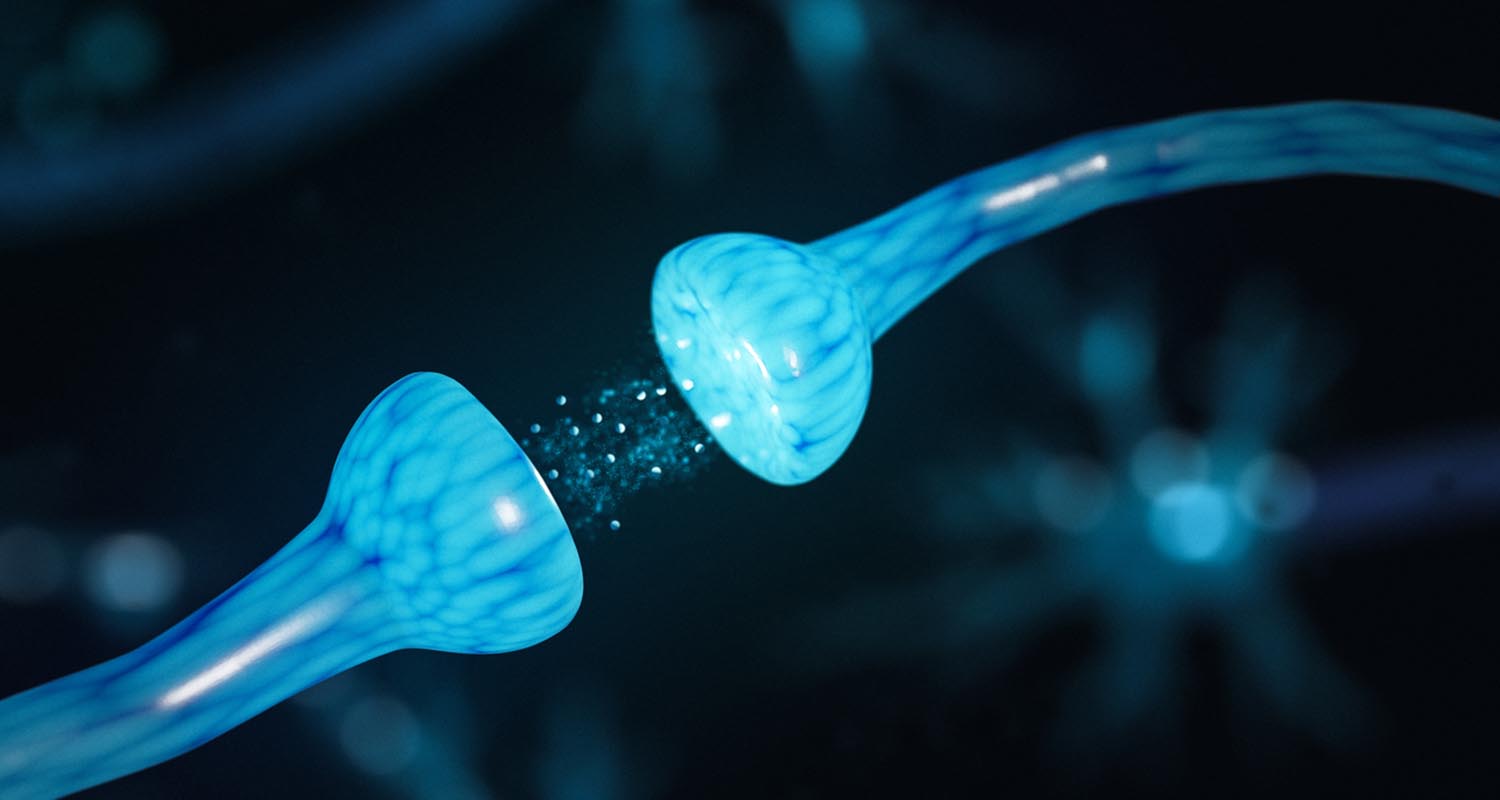 Research into ketamine as a treatment for depression is new, so doctors aren’t entirely sure why ketamine is so effective, particularly for patients who haven’t responded to more traditional treatments — but most doctors believe it’s thanks to the way ketamine interacts with the brain.
Research into ketamine as a treatment for depression is new, so doctors aren’t entirely sure why ketamine is so effective, particularly for patients who haven’t responded to more traditional treatments — but most doctors believe it’s thanks to the way ketamine interacts with the brain.
 Clearly, ketamine infusion therapy is an incredible tool if you’re struggling with major depressive disorder — but that doesn’t mean you should try to take treatment into your own hands.
Clearly, ketamine infusion therapy is an incredible tool if you’re struggling with major depressive disorder — but that doesn’t mean you should try to take treatment into your own hands. There’s a pretty good chance you have a few scars somewhere on your body. (Pierced ears? That’s two, right there.) Scars happen almost every time a scratch or cut gets deep down to the dermal layer of the skin or beyond. They form as a normal part of your body’s tissue repair.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1125033/#B6″]
There’s a pretty good chance you have a few scars somewhere on your body. (Pierced ears? That’s two, right there.) Scars happen almost every time a scratch or cut gets deep down to the dermal layer of the skin or beyond. They form as a normal part of your body’s tissue repair.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1125033/#B6″] Unless you’re super into organ meats, you’re probably not getting much collagen in your diet. Your body can only make collagen if it has the right building blocks to produce it.
Unless you’re super into organ meats, you’re probably not getting much collagen in your diet. Your body can only make collagen if it has the right building blocks to produce it.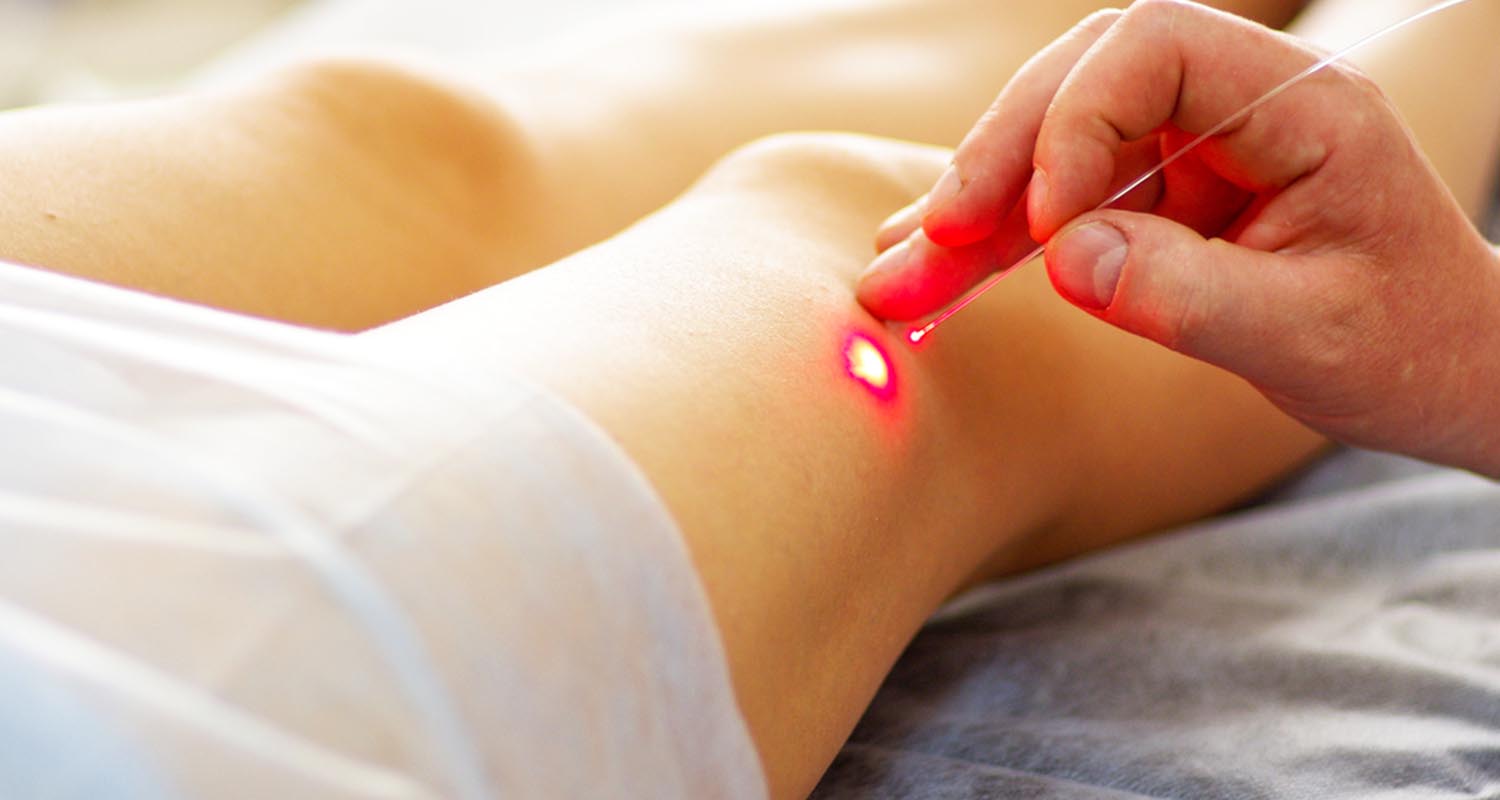 Laser treatment is well-established as an effective treatment for certain types of scarring in only a few treatments.[ref url=”https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2007.33059.x”][ref url=”https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1524-4725.1996.tb00497.x”][ref url=”https://europepmc.org/abstract/med/8192370″] How few? One study showed that raised, red scars less than a year old were completely resolved in less than 3 treatments. Scars over a year old were resolved in less than 5 treatments.[ref url=”https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1524-4725.1995.tb00270.x”]
Laser treatment is well-established as an effective treatment for certain types of scarring in only a few treatments.[ref url=”https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2007.33059.x”][ref url=”https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1524-4725.1996.tb00497.x”][ref url=”https://europepmc.org/abstract/med/8192370″] How few? One study showed that raised, red scars less than a year old were completely resolved in less than 3 treatments. Scars over a year old were resolved in less than 5 treatments.[ref url=”https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1524-4725.1995.tb00270.x”] Systemic enzymes are enzymes that you take in pill form, and they act on your whole body.
Systemic enzymes are enzymes that you take in pill form, and they act on your whole body. A skilled plastic surgeon can work miracles on severely scarred skin. Set up a consultation to discuss what’s possible for your scar treatment. It’s ultimately up to you if you decide to leave it or go through with surgery.
A skilled plastic surgeon can work miracles on severely scarred skin. Set up a consultation to discuss what’s possible for your scar treatment. It’s ultimately up to you if you decide to leave it or go through with surgery.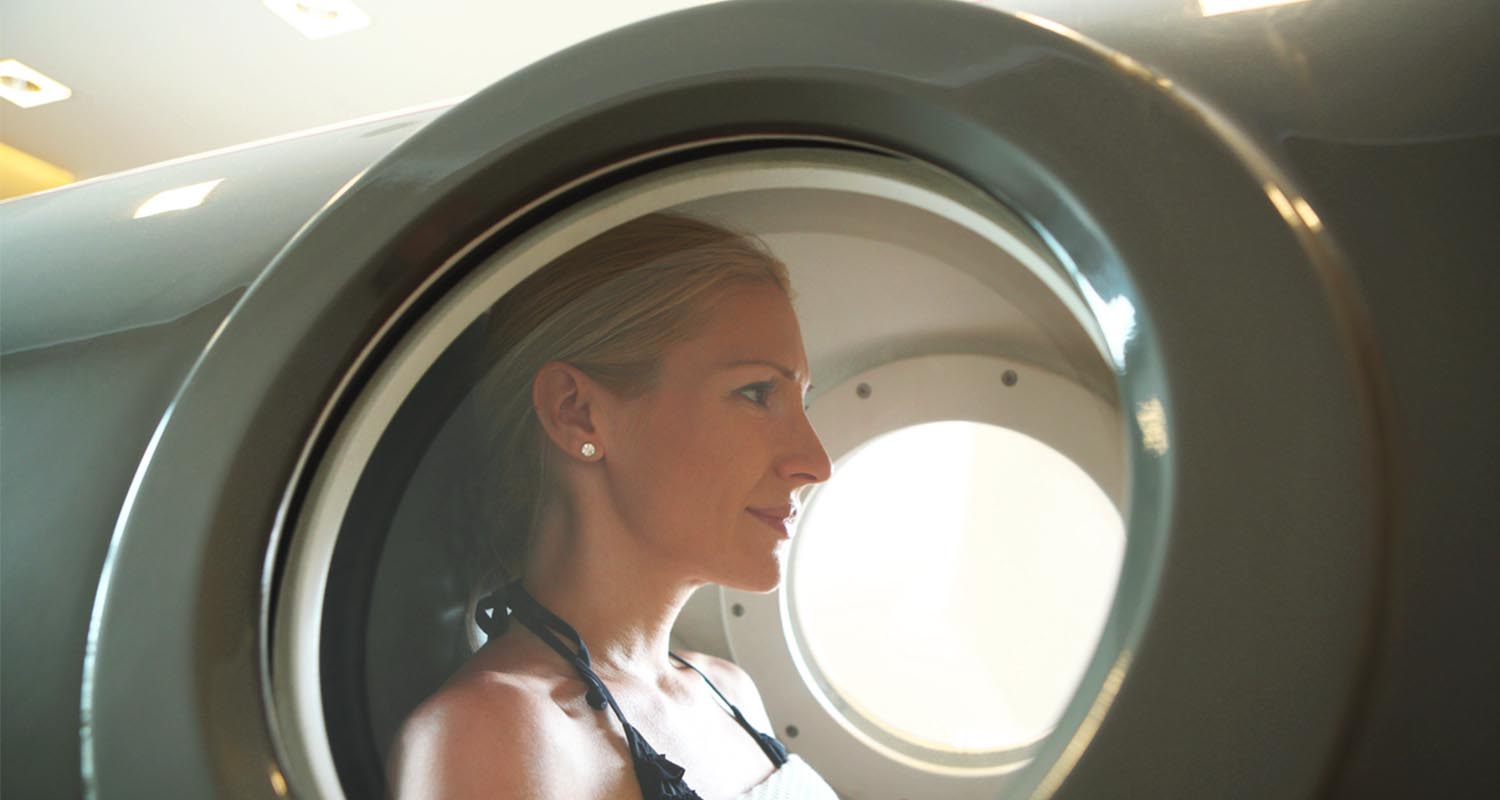 Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) shows promise as part of scar prevention and healing, specifically for severe burns. Not only did HBOT reduce the length of hospital stay for burn victims with significant skin surface area burns,[ref url=”https://academic.oup.com/jbcr/article-abstract/10/5/432/4786434″] it also reduced the need for surgery in up to 80% of burns.[ref url=”http://dspace.rubicon-foundation.org:8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/4369″]
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) shows promise as part of scar prevention and healing, specifically for severe burns. Not only did HBOT reduce the length of hospital stay for burn victims with significant skin surface area burns,[ref url=”https://academic.oup.com/jbcr/article-abstract/10/5/432/4786434″] it also reduced the need for surgery in up to 80% of burns.[ref url=”http://dspace.rubicon-foundation.org:8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/4369″] Trans fats (or trans-fatty acids) are made through the partial hydrogenation of unsaturated fats, which can occur naturally and industrially. Adding hydrogen atoms straightens out the molecular bonds in a fat, making it more solid at room temperature. The food industry uses hydrogenation as a cheap way to make foods last longer on the shelf, enhance their textures, and withstand repeated dunks in the deep fryer.
Trans fats (or trans-fatty acids) are made through the partial hydrogenation of unsaturated fats, which can occur naturally and industrially. Adding hydrogen atoms straightens out the molecular bonds in a fat, making it more solid at room temperature. The food industry uses hydrogenation as a cheap way to make foods last longer on the shelf, enhance their textures, and withstand repeated dunks in the deep fryer. Artificial trans fats are just that: artificial. These are fats that nature never intended to hydrogenate, and your body doesn’t really know what to do with the end product. This leads to chronic inflammation, increasing your risk of stroke, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.[ref url=”http://www.eurekaselect.com/75988/article”] Trans fats raise the ratio of bad LDL to good HDL cholesterol.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20209147″] Studies also link artificial trans fats to various cancers, pregnancy complications, and weaker brain function.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3551118/”][ref url=”http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0128129″]
Artificial trans fats are just that: artificial. These are fats that nature never intended to hydrogenate, and your body doesn’t really know what to do with the end product. This leads to chronic inflammation, increasing your risk of stroke, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.[ref url=”http://www.eurekaselect.com/75988/article”] Trans fats raise the ratio of bad LDL to good HDL cholesterol.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20209147″] Studies also link artificial trans fats to various cancers, pregnancy complications, and weaker brain function.[ref url=”https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3551118/”][ref url=”http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0128129″] So, trans fat foods = bad, right? Most people are surprised to learn that
So, trans fat foods = bad, right? Most people are surprised to learn that  The Dietary Guideline for Americans and the European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention both recommend limiting trans fats to as little as possible, while the European Guidelines specify “preferably no intake from processed food, and <1% of total energy intake from natural origin.”[ref url=”https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/resources/DGA_Recommendations-At-A-Glance.pdf”][ref url=”https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj”] While these recommendations are spot on for industrial trans fats, Dr. Clemens von Schacky, head of preventive cardiology at the University of Munich, warns the generalization of natural trans fats may be harmful: “It is important to note that no evidence is cited supporting the reduction in natural trans fats, so there seems to be simple extrapolation from health effects of industrially produced trans fats to health effects of naturally occurring trans fats.”
The Dietary Guideline for Americans and the European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention both recommend limiting trans fats to as little as possible, while the European Guidelines specify “preferably no intake from processed food, and <1% of total energy intake from natural origin.”[ref url=”https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/resources/DGA_Recommendations-At-A-Glance.pdf”][ref url=”https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj”] While these recommendations are spot on for industrial trans fats, Dr. Clemens von Schacky, head of preventive cardiology at the University of Munich, warns the generalization of natural trans fats may be harmful: “It is important to note that no evidence is cited supporting the reduction in natural trans fats, so there seems to be simple extrapolation from health effects of industrially produced trans fats to health effects of naturally occurring trans fats.”